SCADA
SCADA OVERVIEW
SCADA Systems: The Complete Guide
SCADA Systems: The Complete Guide has been designed to help you to understand what SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) is and how your company can benefit from its implementation. From HD visual displays, remote control, and improved efficiency to unlimited data acquisition, alarming and ERP integration, SCADA opens up your plant floor to today’s leading technologies. In this guide we will break down into manageable parts the various components of a SCADA system, which taken as a whole can be seen as the digitalization of your automation processes. We will dig into the benefits that result from modernizing your legacy systems as well as the challenges that can present themselves during the migration.
"SCADA is a system of software and hardware elements that allows organizations to control and monitor industrial processes by directly interfacing with plant-floor machinery and viewing real-time data."- Inductive Automation
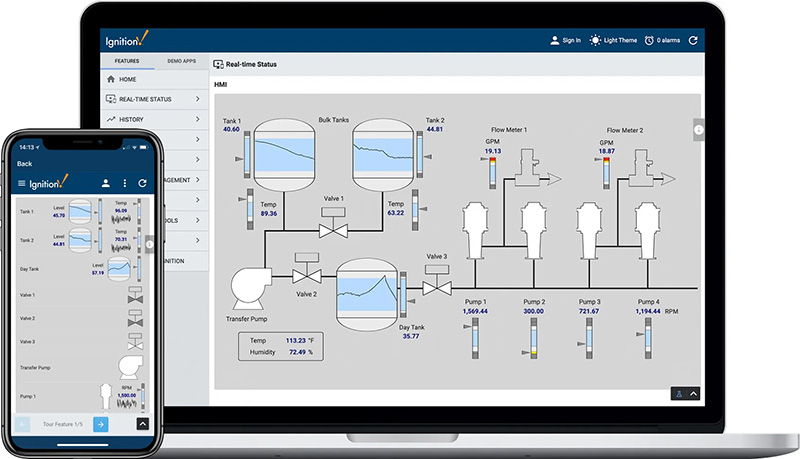
One of SCADAs most talked about features is process control. SCADA integration centralizes displays in one location and reduces the number of HMIs required. This not only provides a clear overview of integrated processes, but also reduces the number of employees necessary to maintain efficient control. This also allows for the implementation of centralized alarming, reducing the chances of unregulated events. Process control through SCADA also gives granulized control over system parameters, starting and stopping equipment and initiating maintenance. Realtime control over inputs through visually intuitive display components gives the SCADA user complete control over equipment spread throughout the facility, or even multiple facilities. Being able to immediately respond to components outside of standard operating parameters or to update recipes based on live data is supervisory control on a game changing level. An important component of the SCADA system is the ability to store data in a wide variety of databases that can easily be accessed by conventional software such as ERPs. Data can be stored locally or in the cloud, data redundancy is more easily achieved, and data can easily become part of a larger digitalization regime. The ERP integration made available through a modern SCADA system is an invaluable tool within any organization for extending important production data to other invested users. This can help management better understand production levels, maintain supply chain requirements and to budget for the future. One important piece to the SCADA puzzle is the historical data that can be stored for future trend analysis, performance benchmarking and predictive maintenance. This historical data can be logged based on user defined events, such as reaching a threshold or when a field is manually updated. This data is timestamped and used in many summary and on-demand reports. Ignition has quickly risen amongst its SCADA software peers due to its unlimited licensing package, but there are a number of other software packages that are common within the industry such as Wonderware, Factory Talk and SCADAPACK to name a few. You may already be invested in one of these packages or another. Whether it benefits your company to switch or stay with what you already have would require a deep dive into your current configuration. It is worth understanding the basic benefits of some of the top SCADA software contenders at the earliest stage possible. The more your company becomes invested in one software, the more cost prohibitive it will become to migrate to another. Having real-time data analysis of processes within the plant from a centralized location is invaluable for efficient control of numerous, often integrated systems. Being able to adjust inputs based on real-time results give the user unmatched control. The prompt fault detection and diagnosis provided by the real-time data of an integrated SCADA system allows for quick rectification. Historical data can also be used to anticipate potential system failures, helping to establish predictive maintenance regime. SCADA data provides insights into operational parameters and can be used to detect deviation from standard performance benchmarks. This information helps to maintain consistent product quality and is often used to comply with industrial regulations. The monitoring and control of hazardous materials in the production process can greatly reduce the risk of serious injury on the plant floor. SCADAs real-time data analysis and alarming is an important safety feature that can greatly reduce costly accidents. It doesn’t take much of a stretch of the imagination to see how the components of a SCADA system can lead to cost savings. Operational efficiency, reduced downtime, improved quality control, preventative maintenance and safety all contribute to reducing costs. Also, SCADA’s centralized approach to supervisory control can also reduce employee hours required to maintain production. ROI can make modernizing and digitalizing through SCADA an easy decision. SCADA systems provide users with vast amounts of operational data. This data can be used for creating clear and concise reports for stakeholders and helps with trend analysis, benchmarking and strategic planning. In order to prevent a situation where your systems reach end of life and are no longer supported, upgrading to a new SCADA System may be essential. Upgrading to a SCADA system may also be necessary in order to integrate dissimilar devices. By abandoning outdated legacy systems you will achieve higher productivity, improved quality and increased flexibility. It's more than a buzzword, digital transformation increases productivity by moving manual processes to automated processes. SCADA systems are at the heart of operational technology (OT), where we find most of the data needed for Digital Transformation. SCADA bridges the gap between OT and information technology (IT), facilitating the seamless flow of data essential for monitoring, control, decision-making, and much more. There are a number of severe challenges that often propel companies to migrate their plant operations to a SCADA system. Low data latency: the time between when an event happens, and the user is made aware of it. Limited access to data due to lack of centralized database storage. Limited transfer of system data to corporate applications. Lack of flexibility and scalability. Just to name a few. Pain points associated with legacy systems eventually outweigh the cost of upgrading to a new SCADA system. Data Redundancy on a Thermal Oxidizer AFi provided an Ignition SCADA solution for a client facing substantial potential data loss risks during network downtimes in their Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer (RTO) control room.SCADA Overview
Process Controll

Data Processing
Databases Supported
ERP Integration
Historical Data Analysis
SCADA Software
Scada Software
SCADA Benefits
Real-Time Data Analysis
Reduced Downtime and Increased Longevity of Assets
Improved Quality Control
Enhanced Safety
Cost Savings
Data Recording and Reporting
Legacy System Upgrades
Importance of Facility Upgrades
Digital Transformation
Common Challenges Facing Legacy Systems
Legacy System Challenges
AFi Systems' Latest SCADA Projects




